Tin Y'all Use Pressure Treated Woods For Interior Framing
Pressure-treated woods is controversial due to its handling with chemical preservatives that are potentially harmful. Some debate that pressure-treated wood tin be used throughout the dwelling house, while others fright this could live hazardous.
It’sec important to be careful amongst your purpose of pressure-treated woods inward your dwelling. While it is required inward roughly areas, it is not allowed in others. Pressure-treated wood must too come across a certain measure to be used safely inside the habitation.

Pressure-treated forest can live used for interior framing. In or so places, such equally bottom plates as well as in sills together with sleepers, it is required past code for the framing to live made from pressure level-treated lumber. There are standards of pressure level treatment aimed at ensuring prophylactic from the chemicals used.
Pressure Treated Wood Can Be Used inward Framing
Not entirely can yous purpose force per unit area-treated woods for interior framing, just in that location are close to locations where preservative-treated woods is actually required according to the residential edifice codes.
Locations Where Preservative Treated Wood Is Required
According to Section R317.1 of the International Residential Code (IRC), sure areas of the dwelling house, peculiarly those that are susceptible to atmospheric condition harm and pests and ask to be durable inwards society to furnish back up, are required to consist of pressure level-treated wood.
Within Crawl Spaces
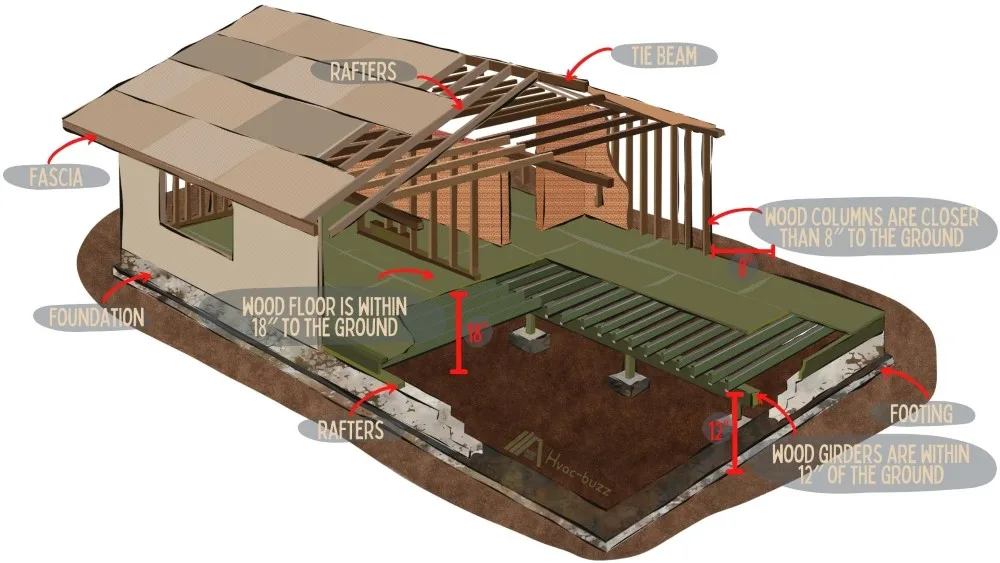
Preservative treated forest is required in crawl spaces where the woods floor is inside 18″ of the ground, where woods girders are within 12″ of the earth, together with where woods columns are closer than 8″ to the earth.
The ground is going to be moist, together with crawl spaces are oft non good protected from the atmospheric condition, and so this makes pressure level-treated forest essential in these areas.
To further protect the crawl infinite from wet, many people install a vapor barrier, or get all out as well as encapsulate it. You tin read nigh each of these in addition to the differences between them inward Differences Between Encapsulation too Vapor Barrier.
Structural Supports of Weather-Exposed Roofs or Decks
Pressure- or preservative-treated woods is required on wood framing that supports moisture-permeable floors or roofs. This is exempt when the roof or flooring is separated from the framing by a wet barrier.
Pressure-treated wood is highly durable together with resistant to rot, making it necessary for withstanding possible wetness too weather harm to susceptible areas. Roofs too decks are both real vulnerable to water impairment due to their directly exposure to the elements.
Sills/Sleepers
Pressure-treated lumber is required for sills as well as sleepers, which contain framing that supports the flooring, where these sills in addition to sleepers have direct contact with the earth. This requirement falls away if the woods frame is separated from the ground by a moisture barrier.
Flooring needs to live protected from dampness too infestation. Pressure-treated wood will go along pests together with wetness from damaging your flooring’second support. If your flooring gets damaged it tin showtime to squeak, and then if your floors are squeaking, don’t but assume that it is normal.
Structural Support of Balconies as well as Porches
Preservative-treated forest is required inwards areas of interior framing that back up balconies, porches, or buildings where their structural elements are exposed to weather outside without protection from the roof or eaves.
Areas that take the potential for water harm are ideal for force per unit area-treated lumber.

Basement Columns (if inwards Contact With Ground)
Basement columns that remainder on the concrete floor call for pressure level-treated wood unless they are raised more than i″ in a higher place the floor alongside a metal barrier together with are separated from the metallic barrier by a moisture barrier.
Basements are notorious for flooding, together with they also call for to live the structural support for the entire habitation in a higher place them. Pressure-treated woods withstands whatsoever dampness inward the basement, which is susceptible to higher levels of humidity.
Using Pressure Treated Wood Throughout House
Pros
- Pressure-treated wood tin can live rattling affordable, more than then than other naturally durable types of lumber. This type of lumber tin come up alongside 30-40% savings.
- It is highly durable, existence resistant to scratches in addition to dents. Pressure-treated woods volition, so, concluding a long time.
- Insects together with pests are not interested inwards pressure level treated woods. This type of lumber is highly unappealing to termites too other insects since making a habitation there would result inward their decease past toxicity.
Cons
- Pressure-treated wood is treated amongst chemical preservatives, including copper, which is linked to the run a risk of cancer. However, the EPA does not deem pressure level-treated woods harmful, and then this is yet upwardly for debate.
- This lumber cannot live cut without proper protection, although Home Depot is happy to cutting for yous. Some meet this equally testify that it is dangerous to purpose inwards the dwelling house.
- Pressure-treated forest cannot be used on countertops or tables. Some too fright that the chemicals used may seep out when used throughout the entire dwelling together with make an unsafe surroundings.
- It is highly flammable, making it a potential rubber gamble. Additionally, the fumes from burned pressure treated woods comprise toxins, so excess woods from habitation structure should not be burned unless by experts.
Anyone considering using force per unit area-treated lumber throughout their habitation must reckon the benefits in addition to disadvantages of this type of woods besides every bit the potential risks. Since pressure-treated wood is non deemed dangerous by the EPA, it is upward to you to determine your persuasion on the subject.
Should Pressure Treated Wood Be Used in Bathrooms?
Pressure-treated forest is nifty for bath floors and walls. Borate-treated forest is highly mutual for bath use because it has been deemed condom past the EPA as well as is highly durable in high moisture settings.
This type of lumber is often used for bathroom subflooring together with places such equally sills where termite infestations tin live common.
Borate-treated lumber may not live completely hazard-gratis since it is treated alongside chemicals, only or so argue that it is safer than other types of preservative-treated forest since it’second a describe mineral establish inwards our H2O.
Is It Hazardous in the Kitchen?
Experts advise against using pressure-treated woods anywhere where it will come up into contact with food. This includes cut boards or dining room tables. However, about people go along to function force per unit area-treated woods in the kitchen.
Pressure-treated woods tin be used anywhere else inward the interior other than places where nutrient touches. This means that kitchen walls in addition to floors are allowed.
Some may decide that having these chemicals in their kitchen seems similar also much of a take a chance inwards instance the chemicals leak from the woods. This is a singular conclusion equally at that place is no rule against its purpose in the space.
Allowable Grade of Pressure Treated Wood
There are standards for the form of pressure-treated forest that tin live used inside of homes for health too condom reasons. The AWPA touchstone is necessary since it includes intensive evaluation and continuous and large-scale information collection of lumber.
The IRC says lumber should run across AWPA U1 standards. This covers many varieties of pressure level-treated wood, their role categories, in addition to their allowable retentions of preservatives (measured inwards pounds per cubic foot of woods).
Interior function woods falls inside the UC1 category (interior dry out) in addition to UC2 category (interior damp). UC1 as well as UC2 take the same retentiveness levels for each of the preservative categories according to AWPA U1 standards.
ACQ- Type B or C
- Alkaline Copper Quarternary
- Retention of .25
ACQ- Type A or D
- Alkaline Copper Quarternary
- Retention of .15
CA-B
- Copper Azole- Type B
- Retention of .10
CA-C
- Copper Azole- Type C
- Retention of .060
Cu8
- Oxine Copper (Copper viii Quinolinolate)
- Retention of .020
CuN-due west
- Waterborne Copper Naphthenate
- Retention of .070
CX-A
- Copper HDO
- Retention of .206
EL2
- DCOI-Imidacloprid-Stabilizer
- Retention of .019
KDS
- Alkaline Copper Bentaine
- Retention of .xix
MCA
- Micronized Copper Azole
- Retention of .060
MCA-C
- Micronized Copper Azole-Type C
- Retention of .050
PTI
- Propiconazole-Tebuconazole-Imidaloprid
- Retention of .013
PTI
- PTI summation Stabilizer
- Retention of .013
SBX
- Inorganic Boron (Formosan termites)
- Retention of .28
SBX
- Inorganic Boron (not-Formosan termites
- Retention of .17
Can I Use a Higher Grade of Treated Wood?
The principal grades of pressure-treated forest include Premium, SS or Select Structural, Grade ane, Grade two, together with Grade 3.
Premium woods is the prettiest wood, containing no knots splits, or blemishes. This type of forest is more often than not Grade 1 or Grade 2 in terms of strength.
Select Structural is the strongest type of wood. It has few knots as well as blemishes just more than than Premium. One knothole is allowable every 4 feet, and splits must be shorter than the width of the board.
Grade ane lumber is stronger than Grade two in addition to Grade 3. One knothole is allowable every 3 feet. Splits are allowable as long equally they are non longer than the width of the board.
Grade ii is weaker than all aforementioned lumber grades. Knotholes are allowable every 2 feet and may measure out upward to 3 ane/ii inches in diameter. Splits may mensurate upwardly to i.5 times the width of the board.
Grade iii is weaker with more than imperfections than whatever of those mentioned to a higher place. It is non suited for anything merely light framing where it volition not live seen.
Grade 2 lumber is acceptable for all aspects of the interior including joists, rafters, sills, sleepers, too framing. Grade one is likewise acceptable for all of these aspects likewise equally being suited for more than visible areas of the home, including decks, railings, as well as siding.
Higher grade woods will be more attractive in addition to stronger, but it volition too be more than expensive. For the interior of a domicile, Grade ii pressure-treated forest volition perform well, in addition to the role of Grade three should live limited.
You Cannot Use CCA-Treated Wood
CCA stands for chromated copper arsenate, which contains chromium, copper, as well as arsenic. Since arsenic is a highly toxic chemical, it is no longer used inwards homes since 2003. However, it is even so produced for function in industrial settings due to its high protection against decay and insects, and then be careful if y'all are sourcing secondhand lumber for your framing.
Ensuring the Quality of the Treated Wood
Pressure-treated wood is regulated for quality and must be marked in addition to inspected by a licensed private. This is specified inside Section R317.two of the IRC.
The IRC specifies that the woods must be approved according to the American Lumber Standard Committee. The inspection way must be approved themselves and will mark the lumber with pregnant aspects of its treatment.
This includes the institute where it was treated, the preservative type used, the minimum preservative memory, the forest’sec stop role, the criterion of its handling, the inspection agency, as well as “dry out” if it has been dried.
Special Fasteners and Connectors Required

Preservative treated wood must be attached amongst specific fasteners that, according to Section R317.iii of the IRC must live
“hot-dipped, zinc-coated galvanized steel, stainless steel, silicone bronze or copper.”
The IRC besides specifies that steel bolts must have ½” or larger diameter too that:
“fasteners other than nails, staples in addition to timber rivets shall live permitted to be of mechanically deposited zinc-coated steel with coating weights inward accordance amongst ASTM B696, Class 55 minimum”.
Additionally:
“manifestly carbon steel fasteners inward SBX/DOT as well as zinc borate preservative-treated woods in an interior, dry surround shall live permitted.”
These specifications are required because the chemicals inwards preservative-treated forest can live corrosive to sure types of metal. The permitted types of fasteners are resistant to corrosion.
Different types of chemicals used to process woods tin be less corrosive, which is why an exception is made for zinc borate treated wood that regular carbon steel fasteners are acceptable.
Alternatives to Pressure Treated Wood?
Certain types of decay-resistant lumber make proficient alternatives to force per unit area-treated woods that make not accept whatsoever of the health risks associated amongst the chemical handling.
These include white cedar, redwood, yew, tamarack, hemlock, as well as xanthous cypress. However, these woods are not generally as durable as pressure-treated wood.
Furthermore, government note that force per unit area-treated woods is required by code inward areas of the dwelling house listed higher up. Alternatives are exclusively to live used where this woods is not required.
For not-structural uses, such equally decks, plastic and composite lumber are not bad alternatives to pressure level-treated forest.
If y'all are framing your basement, so an option to using pressure level-treated wood would live to install the framing alongside a 4″ gap betwixt the woods too the masonry wall.
Sources
https://www.fpl.fs.fed.us/documnts/techline/whats-inwards-that-pressure level-treated-wood.pdf
https://www.panna.org/sites/default/files/imported/files/GRCAlternatives2TreatedWood.pdf
https://plasticinehouse.com/force per unit area-treated-lumber-grades/


Comments
Post a Comment